Welcome to our blog post about How to create a Local Admin with Microsoft Intune. In this article, we’ll explore the best practices for creating a local administrator on windows devices, helping you to get the most out of Microsoft Intune. Whether you’re new to Intune or looking to enhance your existing setup, these tips will guide you toward a more secure and efficient management experience. Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
What are we going to set up?
There are multiple options available on how you can create local Administrator accounts with the help of Microsoft Intune. Unfortunately there is no configuration profile where you can create a local administrator account. Here is a quick overview of the options:
- Option 1: OMA-URI Settings: This new option lets you create a local Administrator account with the help of OMA-URI Settings.
- Option 2: PowerShell script: You can create a PowerShell script which we can deploy with Microsoft Intune. This will create the defined local Administrator account on all devices assigned.
We will show you both options how you can configure it in Microsoft Intune.
Option 1: How to create a local Administrator with OMA-URI Settings
In this section we will show you, How you can create a local Administrator with the help of the OMA-URI Settings. This is very simple trust me. Just follow the steps below.
I have also created a youtube video with step-by-step instructions. Just have a look there.
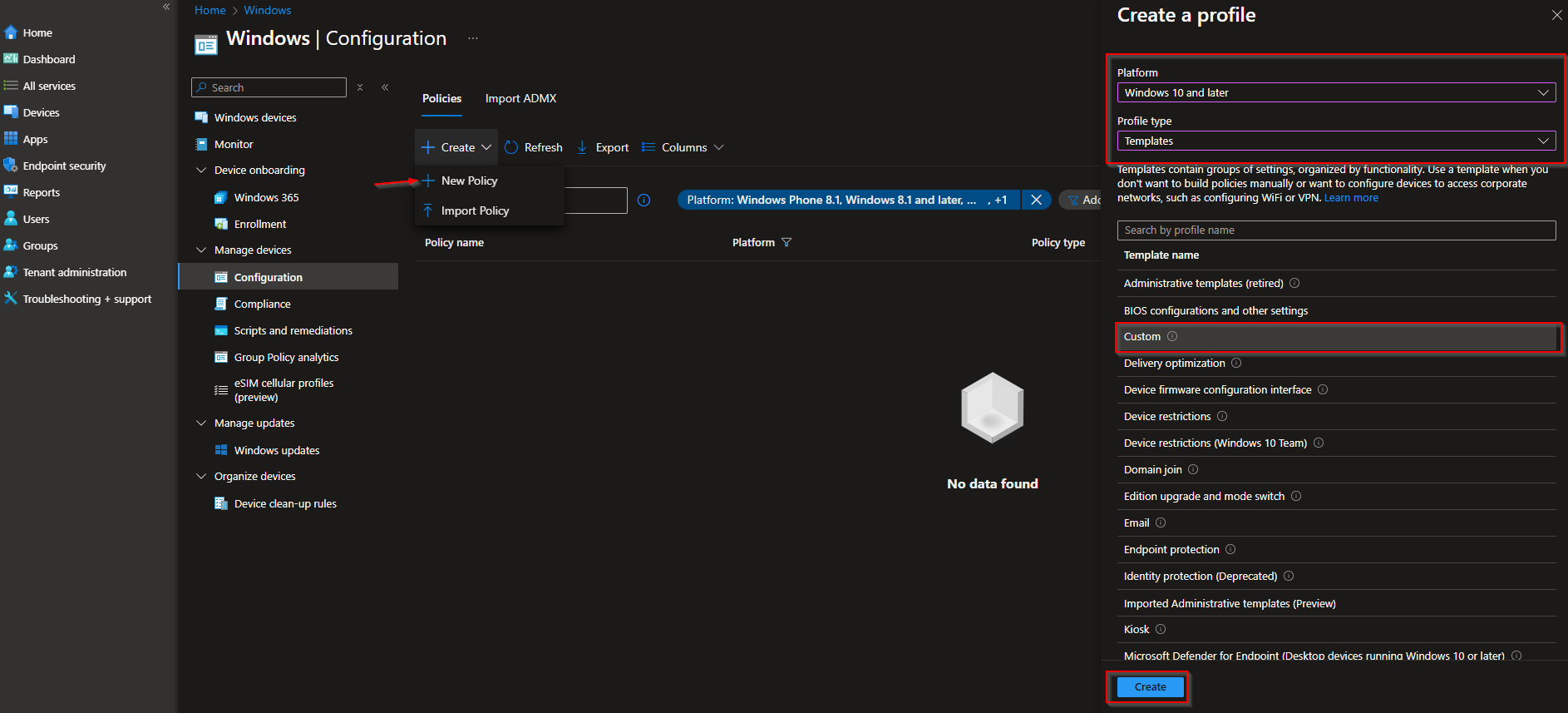
In the first step we will need to create a new Configuration Policy. So login with your Intune Admin and let’s start.
- Go to intune.microsoft.com
- Click on Devices
- Click on Windows
- Click on Configuration profiles
- Click on Create
- Click on New Policy
- Platform: Windows 10 and later
- Profile type: Templates
- Click on Custom
- Click on Create
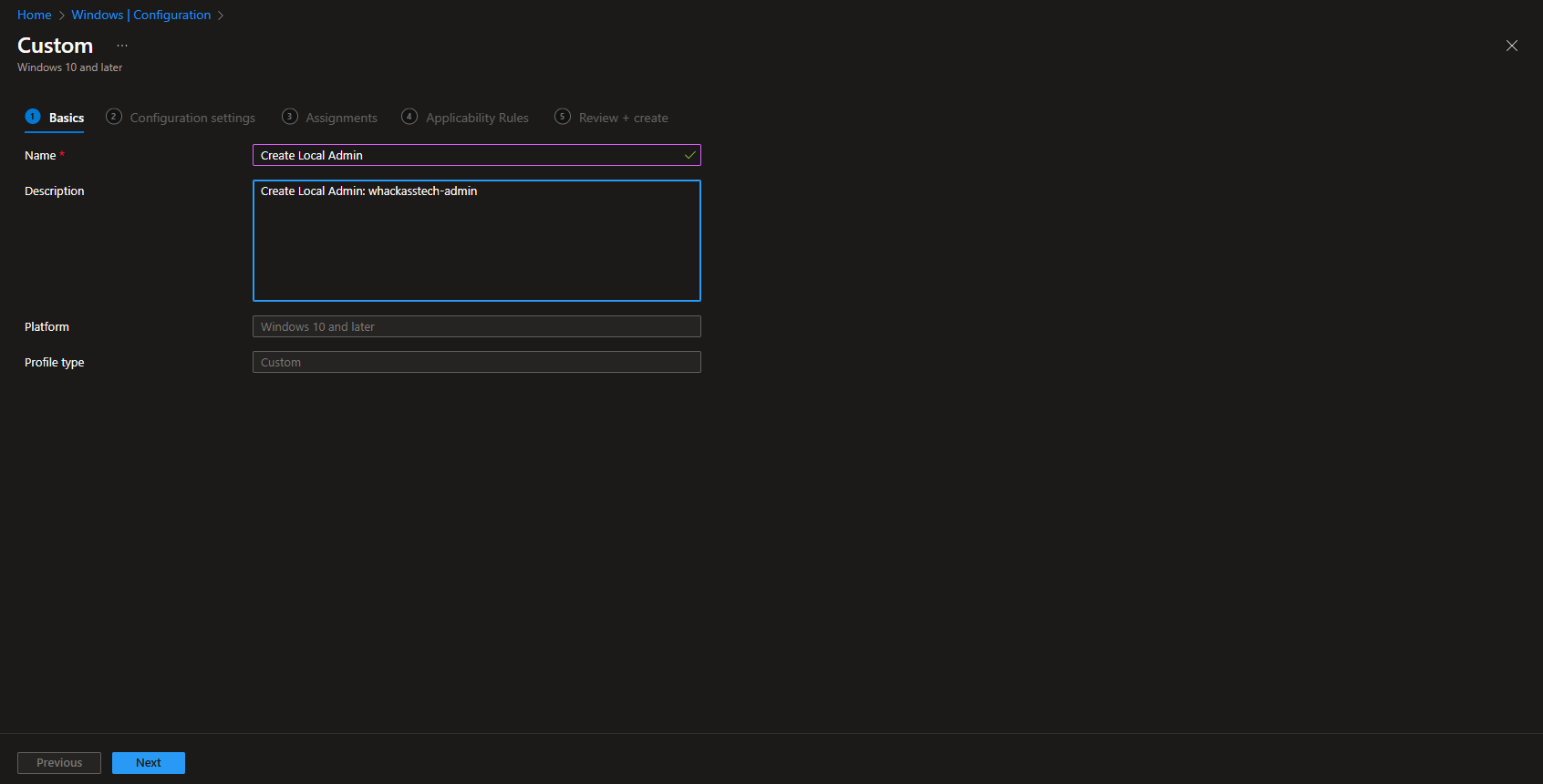
Give it a meaningful name and description. Click on Next.
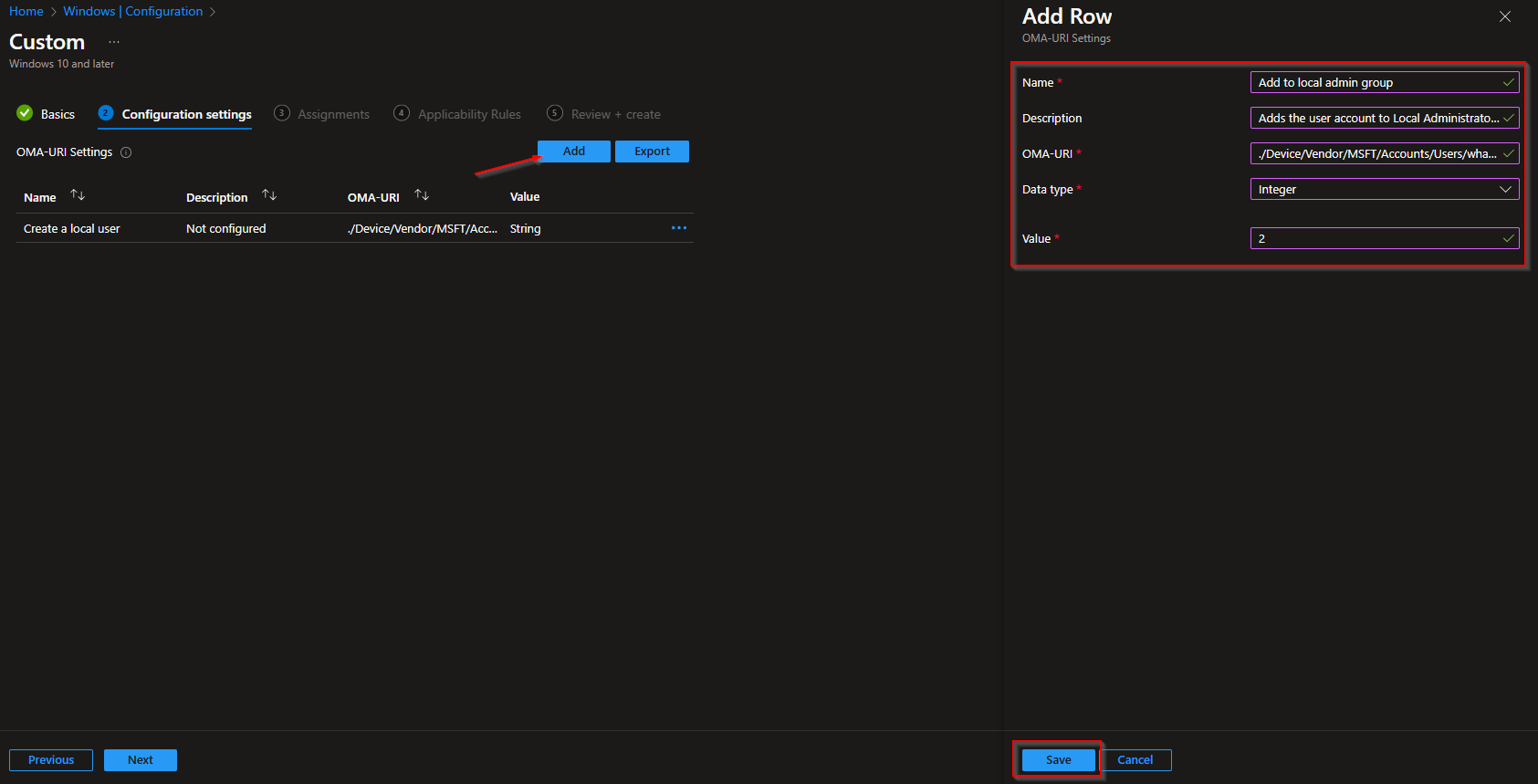
On the Configuration settings tab we need to create two OMA-URI settings. First one will be creating the Local User on the device. The second one will add the User to the local Admininstrator Group. Just follow the steps.
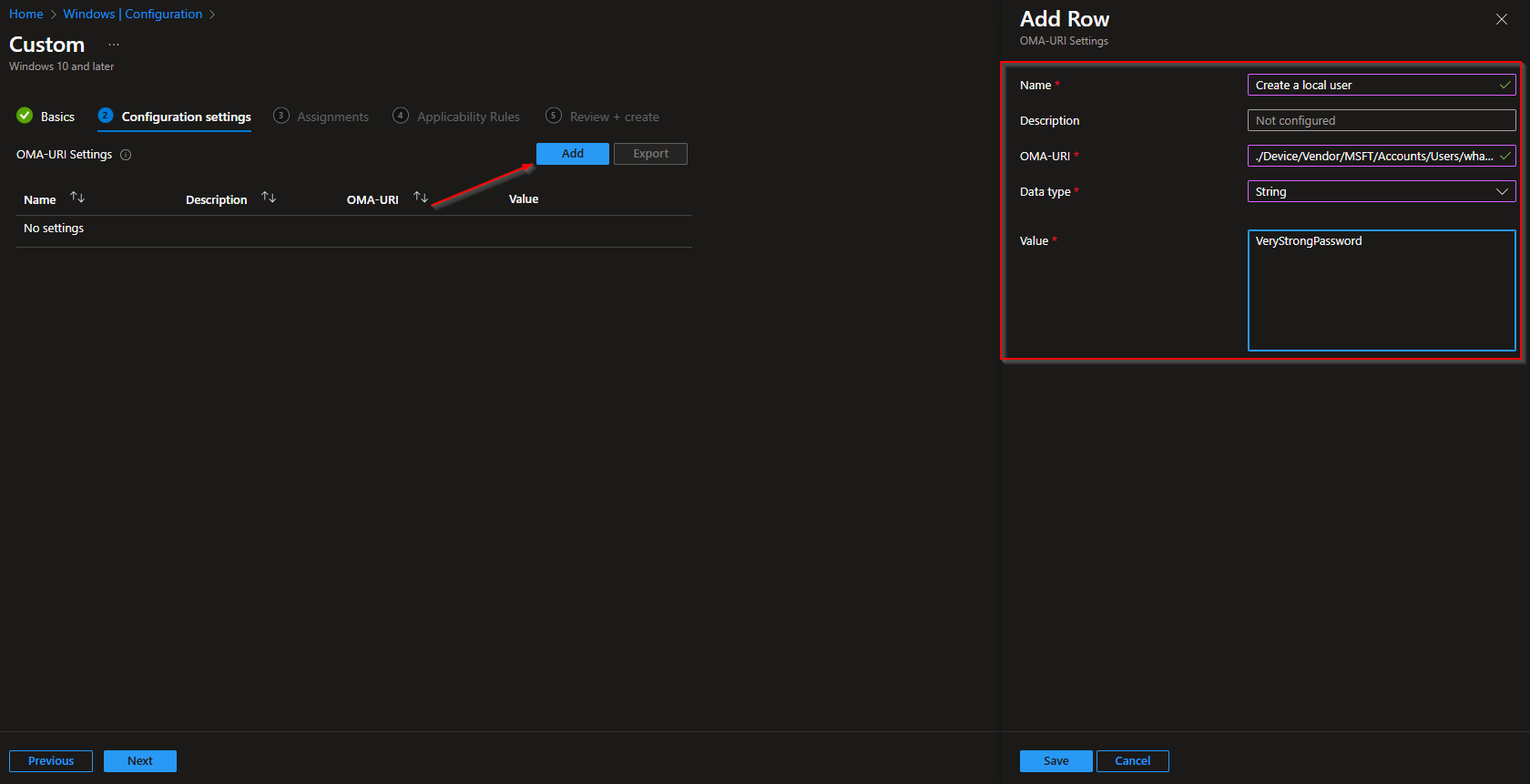
OMA-URI Setting to Create Local Admin Account and Set Password
- Name: Create local user
- Description: This is optional, but you can add a short description
- OMA-URI: ./Device/Vendor/MSFT/Accounts/Users/LocalAdmin/Password
Replace the red part with your Local Admin username. In my case I will name my admin account whackasstech-admin. - Data Type: String
- Value: Specify a password for the local admin account.
OMA-URI Setting for adding account to local administrator group
- Name: Add to local admin group
- Description: Adds the user account to Local Administrators Group
- OMA-URI: ./Device/Vendor/MSFT/Accounts/Users/LocalAdmin/LocalUserGroup
Replace the red part with your Local Admin username. In my case I will name my admin account whackasstech-admin. - Data Type: Integer
- Value: 2
If you have added both OMA-URI settings you can click on Next. Just make sure you have put the same local admin username in the OMA-URI strings.
- On the Assignment tab assign the Policy to a Group or to All Users / All Devices and click on Next
- Define your Applicability Rules if applicable and click on Next
- Review + Create the Policy
Congratulations! You have successfully deployed a local admin with Microsoft Intune. Important: In my case the deployment of the configuration policy gave some Errors. This is normal. The local admin should still be created.
Option 2: How to create a local Administrator with a PowerShell script
Step 1: Create PowerShell script
We will first create a PowerShell script. Follow these steps:
- Create a PowerShell script
- Copy the following scripts:
### Parameter ### $userName = "[ADMINISTRATOR NAME]" $userDescription = "Local Administrator" $password = "[PASSWORD]" ### Check For User ### $checkForUser = (Get-LocalUser).Name -Contains $userName ### Create User When Check is False ### if ($checkForUser -eq $False) { Write-Host "$userName does not exist" $PASSWORD= ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText -Force -String $password New-LocalUser -Name $userName -Description $userDescription -Password $PASSWORD Add-LocalGroupMember -Group "Administrators" -Member $userName } ElseIf ($checkForUser -eq $True) { Write-Host "$userName does exists" }
- Specify the Password [PASSWORD] and the Administrator name [ADMINISTRATOR NAME]
- Save this PowerShell script. I named it “CreateLocalAdmin.ps1
- We need this script in Step 2.
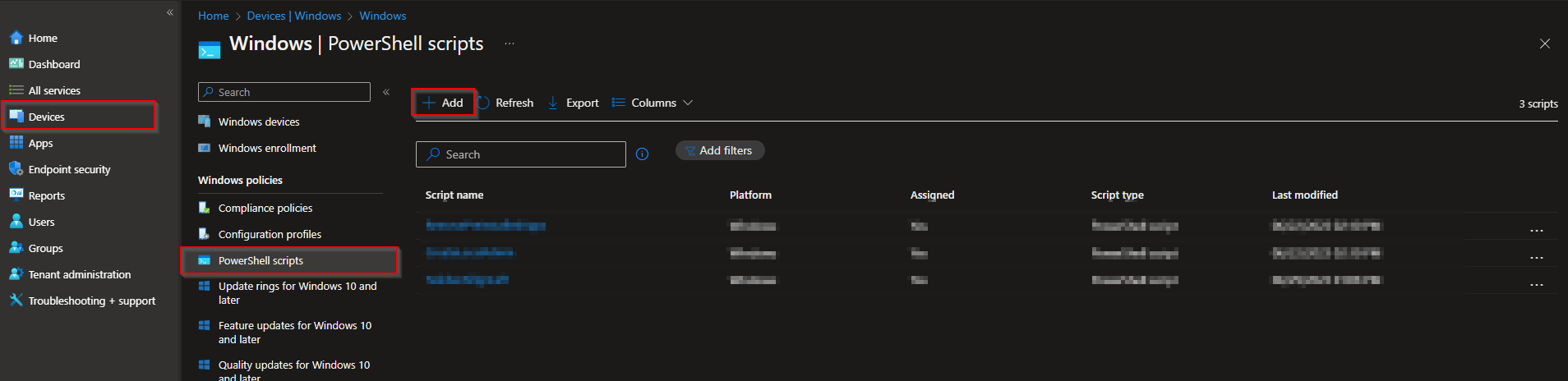
Step 2: Import and deploy with Intune
- Go to intune.microsoft.com
- Click on Devices
- Click on Windows
- Click on PowerShell scripts
- Click on Add
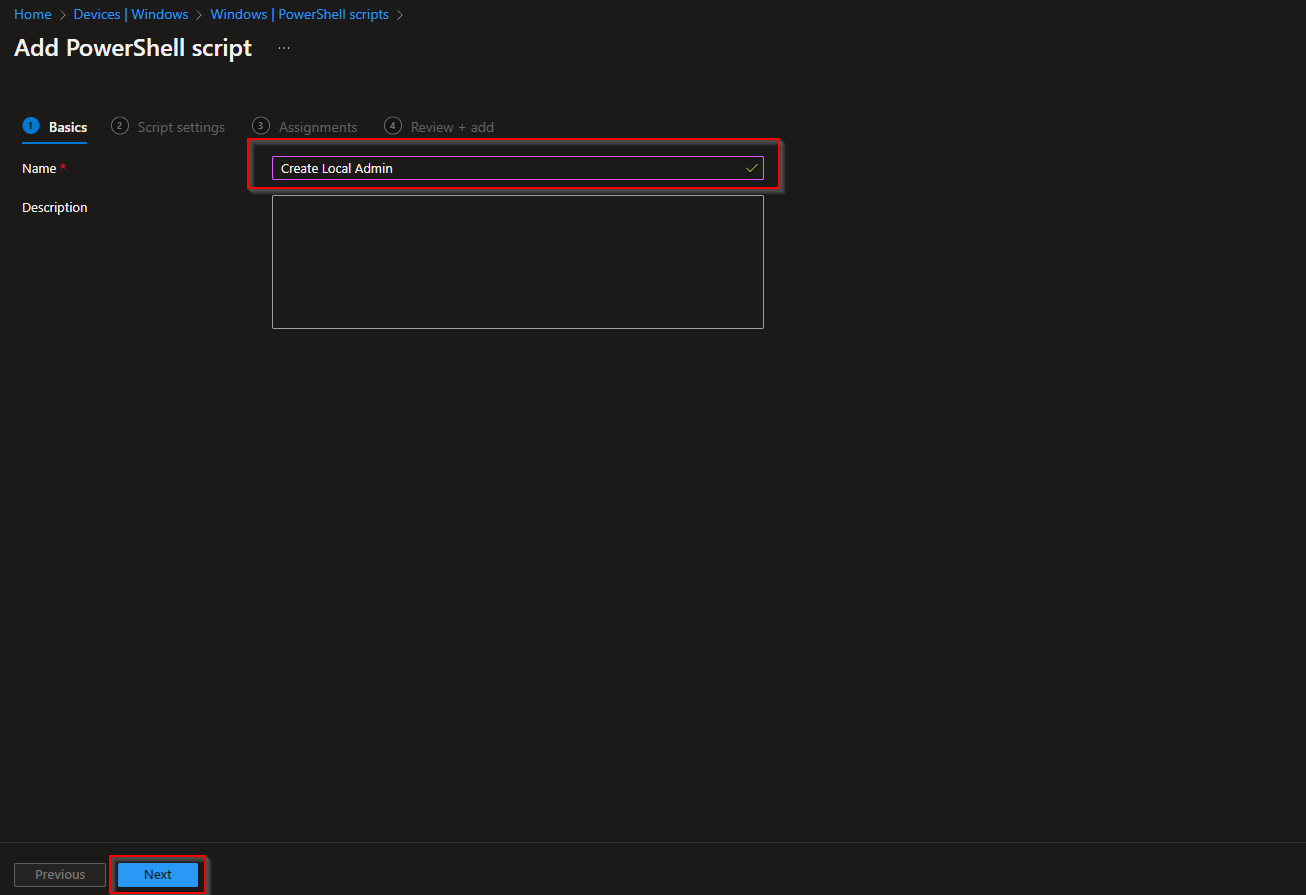
- Give the Policy a name. For example: Create Local Admin
- Click on Next
- Upload your script
- Run this script using the logged on credentials: No
- Enforce script singature check: No
- Run script in 64 bit PowerShell Host: Yes
- Click on Next
- Assign it to a Group
- Click on Next
Congratulations! You have successfully deployed the policy.
Learn about LAPS
LAPS, or Local Administrator Password Solution, is a Microsoft tool that allows organizations to securely manage the local administrator passwords of their computers. In many organizations, all computers are set up with a default local administrator account. If this password is the same across multiple machines, it poses a security risk. If one machine is compromised, the attacker could potentially access all machines with the same administrator password.
LAPS addresses this issue by automatically managing the password for the local administrator account on each computer.












what is difference if we set local user and password via OMA-URI and power shell script
Intune and global administrators will have administrator access on Intune managed devices